When it comes to office chair maintenance, understanding the intricacies of the disconnect switch wiring diagram is crucial for efficient and safe operation. This fundamental knowledge can be the difference between a smooth, trouble-free experience and a frustrating, potentially hazardous situation. In this article, we will delve into the world of office chair wiring, exploring the master disconnect switch wiring diagram in detail, ensuring that you are equipped with the necessary information to tackle any issues that may arise.
Master Disconnect Switch Wiring Diagram is a critical component in the overall functioning of an office chair. It serves as a safety mechanism, allowing users to disconnect the chair from its power source when not in use, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. By understanding how to wire this switch correctly, you can ensure a safe and efficient working environment. In the following sections, we will examine the wiring diagram in greater detail, providing step-by-step instructions and diagrams to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the process[1].
what are the key components of a master disconnect switch
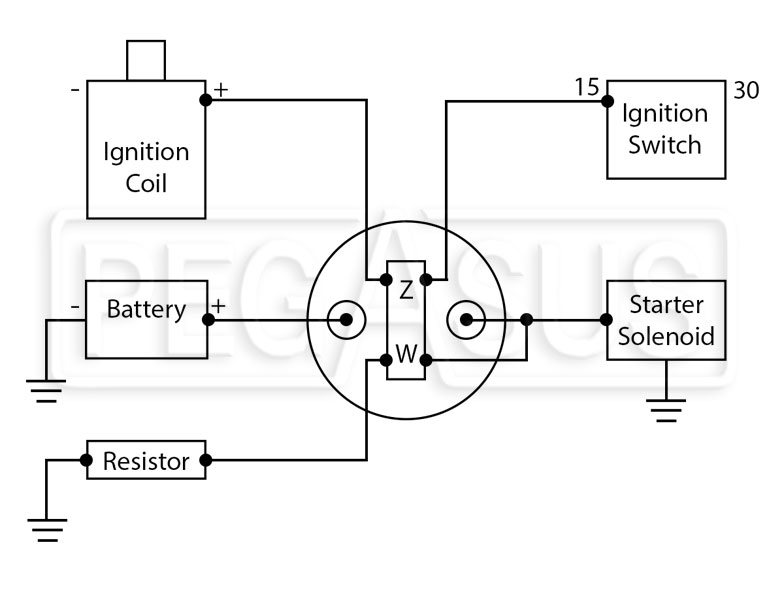 The key components of a master disconnect switch include:
Body: The main housing of the switch, typically made of a durable material such as polycarbonate or die-cast aluminum, designed to withstand environmental conditions and provide a secure mounting base.
Terminals: These are the metal contacts that connect to the electrical circuits being controlled. They are usually made of copper or brass and are designed for high-amp applications. The terminals are secured with nuts and washers to prevent loose connections.
Lever or Handle: This is the part of the switch that is operated by the user to turn the power on or off. It is typically designed for ease of operation and may include features such as anti-rotation indexing posts to prevent accidental disconnection.
Seals and Gaskets: These are used to prevent moisture and dust from entering the switch, ensuring reliable operation and protecting against electrical fires.
Mounting Hardware: This includes the nuts, washers, and screws used to secure the switch to a mounting surface, ensuring a secure and stable installation.
Electrical Contacts: These are the internal components that make and break the electrical connections. They are designed to withstand high currents and are typically made of silver-plated or copper materials.
Wiring Diagrams: These are the detailed illustrations that show how the switch is connected to the electrical circuits it controls. They are essential for proper installation and operation.
These components work together to provide a reliable and efficient means of disconnecting power to electrical systems, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of damage or electrical fires.
The key components of a master disconnect switch include:
Body: The main housing of the switch, typically made of a durable material such as polycarbonate or die-cast aluminum, designed to withstand environmental conditions and provide a secure mounting base.
Terminals: These are the metal contacts that connect to the electrical circuits being controlled. They are usually made of copper or brass and are designed for high-amp applications. The terminals are secured with nuts and washers to prevent loose connections.
Lever or Handle: This is the part of the switch that is operated by the user to turn the power on or off. It is typically designed for ease of operation and may include features such as anti-rotation indexing posts to prevent accidental disconnection.
Seals and Gaskets: These are used to prevent moisture and dust from entering the switch, ensuring reliable operation and protecting against electrical fires.
Mounting Hardware: This includes the nuts, washers, and screws used to secure the switch to a mounting surface, ensuring a secure and stable installation.
Electrical Contacts: These are the internal components that make and break the electrical connections. They are designed to withstand high currents and are typically made of silver-plated or copper materials.
Wiring Diagrams: These are the detailed illustrations that show how the switch is connected to the electrical circuits it controls. They are essential for proper installation and operation.
These components work together to provide a reliable and efficient means of disconnecting power to electrical systems, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of damage or electrical fires.what are the differences between S.P.S.T. and D.P.S.T. master disconnect switches
what are the main applications for SPST and DPST master disconnect switches
The main applications for Single Pole Single Throw (SPST) and Double Pole Single Throw (DPST) master disconnect switches are: SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) Simple on-off tasks: SPST switches are commonly used for basic on-off control of a single circuit, such as in table lamps, appliances, or other simple devices. Single circuit control: They are suitable for controlling a single circuit, like a fan or a light, where only one path needs to be switched on or off. Low-voltage DC devices: SPST switches are often used in low-voltage DC devices where only one leg of the power supply needs to be switched on or off. DPST (Double Pole Single Throw) Controlling multiple circuits: DPST switches are designed to handle two separate circuits, making them suitable for applications where multiple signals need to be controlled simultaneously, such as in industrial settings or control rooms. Fail-over capabilities: DPST switches are used in redundant signaling applications where a fail-over circuit is necessary in case of signal loss from the first circuit. Higher switching currents: DPST switches can handle higher currents and are commonly used in applications such as controlling relays, pumps, and drive motors. Industrial and commercial settings: DPST switches are used in industrial and commercial settings where multiple circuits need to be controlled, ensuring safety and efficiency in these environments. These applications highlight the differences in functionality and usage between SPST and DPST master disconnect switches, with SPST being more suitable for simple on-off tasks and DPST for more complex applications involving multiple circuits. #EANF#As we conclude our exploration of the master disconnect switch wiring diagram, we hope that you have gained valuable insights into the intricacies of office chair maintenance. Understanding the importance of proper wiring and the role of the disconnect switch in ensuring safety and efficiency is crucial for any individual or organization utilizing office chairs. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your office chairs are properly maintained and that you are equipped to handle any issues that may arise.
Remember, a well-maintained office chair is not only a matter of comfort but also a matter of safety. The disconnect switch is a critical component in ensuring that the chair is properly disconnected from its power source when not in use, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. By staying informed about the proper wiring and maintenance of your office chairs, you can ensure a safe and efficient working environment. We encourage you to continue exploring and learning about the various aspects of office chair maintenance, and we wish you the best in your endeavors to create a comfortable and safe workspace. Thank you for joining us on this journey into the world of office chair maintenance, and we hope that you will continue to find our content informative and helpful in your daily work.
No comments:
Post a Comment